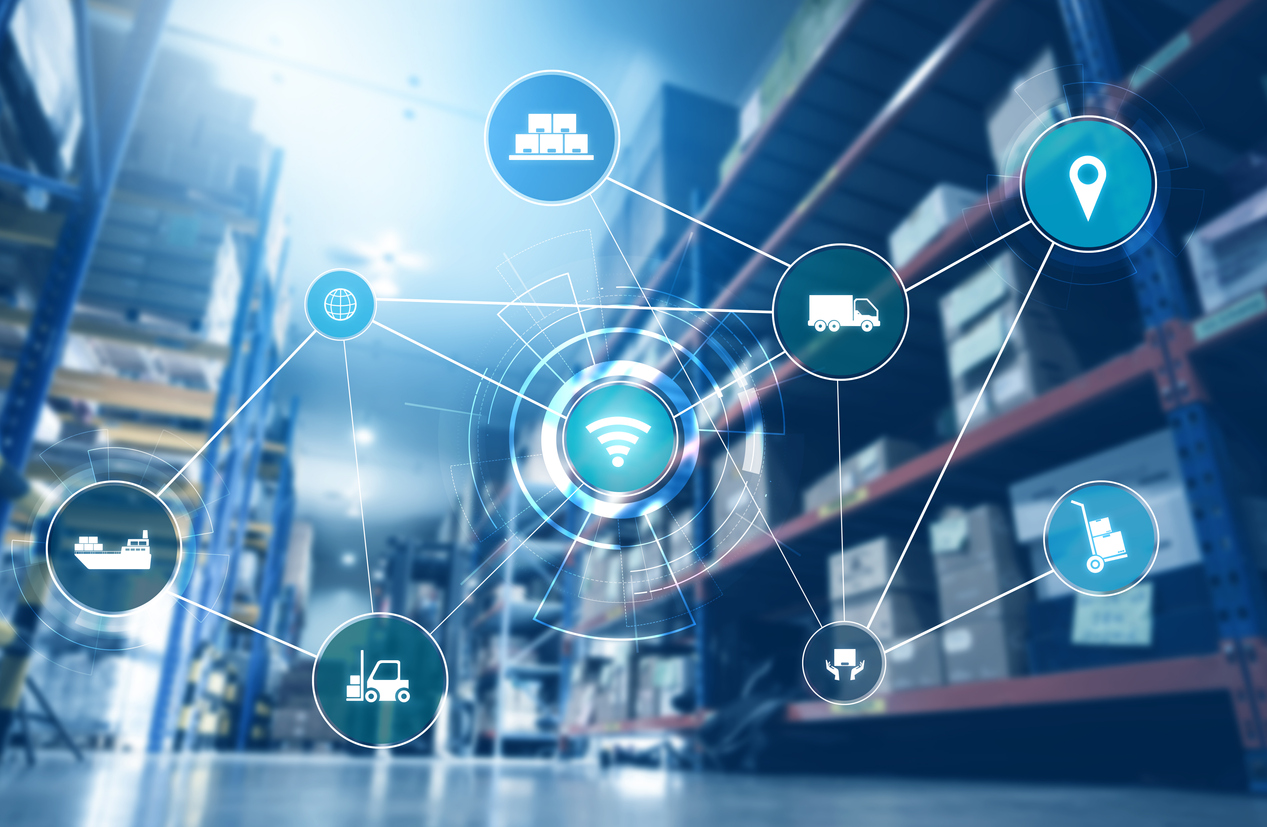

Logistics refers to the movement of goods from production to final delivery. Many organizations, people and activities are involved in logistics to make goods easily available for purchase. A logistics supply network is a collaborative effort of multiple stakeholders. While logistics is often the primary focus of many companies, it can also include software and transportation. Here are some examples of different logistical systems. You can read on to learn about these systems and how you can improve your company’s supply chain operations.
Logistics is the movement and storage of goods from their initial production through final delivery.
Logistics refers to the efficient movement of goods from their initial production through final delivery. By optimizing flow, products can reach their customers at a precise time, at the best place, and at a reasonable cost. The following are 7 "rights" of logistics. One of these is the right time. Customers should receive products at the correct time and in the right conditions.
Inbound logistics considers the inbound movement products and materials to manufacturers. On the other hand, outbound logistics examines the outbound flow of goods or information from outside of the business. Inbound logistics involves acquiring materials and arranging for inbound transportation and storage. Reverse logistics is the return shipment and packaging of finished products. It also includes the management of remaining inventory and, in certain cases, the disposal and reuse of waste.
It is a well-respected business.
The term risk-adjusted investing (RAR), refers to the use of capital or funds that take on more risk than normal business investments. The opportunity cost of risk is the difference between risk-adjusted and normal business investment yields. RAR helps business owners to manage cash flows in different areas of their business, and reduces the risk of investment.
It is a limited part of a larger, collaborative supply chain
A highly integrated supply network is one that includes many suppliers who rely on timely deliveries. In such a chain, failure to deliver could bring the whole chain to a halt. Even the best logistics providers or suppliers can't avoid all disruptions. To ensure that every participant in the chain functions smoothly and efficiently, it's important to evaluate the risks involved in each system.
Both retailers and manufacturers can benefit from a partnership. For example, a recent collaboration between a retailer and a large U.S. retail chain resulted in a reduced logistics cost between the factory and the store. This collaboration can also increase retailers' sales. Manufacturers can also collaborate with retailers to lower transportation and labor costs.
It involves software
Companies can manage their entire supply chain by using supply management software. The software manages all aspects of the supply chains, from vendor relationships to transactions. Supply chain management software can be used by any size business. These programs can be used to manage inventory, supplier relationships, data flow, and other business functions. These programs can cover all stages of product development including warehousing, shipping, and distribution. They can also manage inventory and provide insight into trends and demand.
Logistics software can be used to improve inventory management, fleet management and communication. It can also enhance customer service. It automates daily tasks, and transforms data into useful insights for business owners. It can also improve inventory and communication processes, which are crucial to successful management of supply chains. These applications can increase customer service and profitability. If you're thinking about purchasing software for an enterprise, here are some benefits.
FAQ
What is Six Sigma?
It is a way to improve quality that places emphasis on customer service and continuous learning. The goal is to eliminate defects by using statistical techniques.
Motorola invented Six Sigma in 1986 as part its efforts to improve manufacturing.
The idea spread quickly in the industry. Today many organizations use six-sigma techniques to improve product design.
What is Kaizen, exactly?
Kaizen, a Japanese term that means "continuous improvement," is a philosophy that encourages employees and other workers to continuously improve their work environment.
Kaizen is founded on the belief of everyone being able to do their job well.
What are the steps of the management decision-making process?
The decision-making process of managers is complicated and multifaceted. This involves many factors including analysis, strategy and planning, implementation, measurement and evaluation, feedback, feedback, and others.
Remember that people are humans just like you, and will make mistakes. This is the key to managing them. You are always capable of improving yourself, and there's always room for improvement.
We explain in this video how the Management decision-making process works. We will discuss the various types of decisions, and why they are so important. Every manager should be able to make them. The following topics will be covered.
What are the 4 main functions of management?
Management is responsible for planning, organizing, directing, and controlling people and resources. This includes setting goals, developing policies and procedures, and creating procedures.
Management aids an organization in reaching its goals by providing direction and coordination, control, leadership motivation, supervision, training, evaluation, and leadership.
The following are the four core functions of management
Planning - Planning involves determining what needs to be done.
Organizing: Organizing refers to deciding how things should work.
Directing - Directing means getting people to follow instructions.
Controlling – This refers to ensuring that tasks are carried out according to plan.
What is the role of a manager in a company?
Different industries have different roles for managers.
A manager is generally responsible for overseeing the day to day operations of a company.
He/she will ensure that the company fulfills its financial obligations.
He/she is responsible for ensuring that employees comply with all regulations and follow quality standards.
He/she plans and oversees marketing campaigns.
Statistics
- Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees (upcounsel.com)
- This field is expected to grow about 7% by 2028, a bit faster than the national average for job growth. (wgu.edu)
- Your choice in Step 5 may very likely be the same or similar to the alternative you placed at the top of your list at the end of Step 4. (umassd.edu)
- The BLS says that financial services jobs like banking are expected to grow 4% by 2030, about as fast as the national average. (wgu.edu)
- UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers on its site. (upcounsel.com)
External Links
How To
How can you implement a Quality Management Plan?
QMP (Quality Management Plan) is a system to improve products and services by implementing continuous improvement. It provides a systematic approach to improving processes, products and customer satisfaction by continuously measuring, analysing, controlling, controlling, and improving them.
QMP stands for Quality Management Process. It is used to guarantee good business performance. QMP improves production, service delivery, as well as customer relations. QMPs should address all three dimensions: Products, Services, and processes. The QMP that only addresses one aspect of the process is called a Process QMP. The QMP that focuses on a Product/Service is called a "Product." QMP. And when the QMP concentrates on Customer Relationships, it is called "Customer" QMP.
There are two key elements to implementing a QMP: Strategy and Scope. They can be described as follows:
Scope is what the QMP covers and how long it will last. For example, if your organization wants to implement a QMP for six months, this scope will define the activities performed during the first six months.
Strategy: This describes the steps taken towards achieving the goals set forth in the scope.
A typical QMP consists of 5 phases: Planning, Design, Development, Implementation, and Maintenance. The following describes each phase.
Planning: This stage determines the QMP goals and prioritizes them. To get to know the expectations and requirements, all stakeholders are consulted. Once the objectives and priorities have been identified, it is time to plan the strategy to achieve them.
Design: During this stage, the design team develops the vision, mission, strategies, and tactics required for the successful implementation of the QMP. These strategies are put into action by developing detailed plans and procedures.
Development: This is where the development team works to build the capabilities and resources necessary for the successful implementation of the QMP.
Implementation: This involves the actual implementation of the QMP using the planned strategies.
Maintenance: This is an ongoing procedure to keep the QMP in good condition over time.
Several additional items should be added to the QMP.
Stakeholder Involvement: Stakeholders are important for the success of the QMP. They need to be actively involved in the planning, design, development, implementation, and maintenance stages of the QMP.
Project Initiation: It is essential to have a clear understanding about the problem and the solution before you can initiate a project. This means that the initiator should know why they want something done and what they hope for from the end result.
Time Frame: It is important to consider the QMP's time frame. The simplest version can be used if the QMP is only being implemented for a short time. However, if you have a long-term commitment, you may require more elaborate versions.
Cost Estimation is another important aspect of the QMP. You can't plan without knowing how much money it will cost. The QMP should be cost-estimated before it can begin.
The most important thing about a QMP is that it is not just a document but also a living document. It can change as the company grows or changes. It should therefore be reviewed frequently to ensure that the organization's needs are met.